Project Description
Project Background
The power station, located in Ashkelon, Israel, is owned by an independent power producer in Israel that supplies electricity via the national power grid to public, business, and commercial entities in the country. It is a combined cycle power station, powered by natural gas, and is the second largest independent power station in the country. It can generate up to a total of 840 megawatts of electricity.
The OEM in this project is one of the veteran companies in the field of desalination, water, and wastewater treatment.
The client required demineralized water for its boiler application. The water source is city water supply, which is filtered through multimedia filters, followed by two pass reverse osmosis, with final polishing by electrodeionization (EDI).
Electrodeionization is continuous, chemical-free process that removes ionized and ionizable impurities from the feed water using DC power. EDI is most commonly used to treat Reverse Osmosis (RO) permeate and replaces Mixed Bed (MB) ion exchange; producing high purity water of up to 18 M Ω.cm.
EDI eliminates the need to store and handle hazardous chemicals required for MB ion exchange resin regeneration and associated waste neutralization steps. EDI also has lower space requirement, low operating cost, and a quick payback. In addition, it provides constant uninterrupted high-quality feed water to the plant.
Fractional Electrodeionization (FEDI) is an advancement of EDI technology that was developed to address the limitations of conventional EDI. EDI is a patented two stage process that operates in a dual voltage configuration that reduces hardness scaling that may occur in conventional EDI.
FEDI’s unique design maintains an acidic condition in the first stage and basic condition in the second stage of the EDI concentrate chamber. This patented design reduces mineral scaling in the first stage and enhances silica removal in the second stage.
FEDI Model: FEDI 2 30X SV
No. of Streams: 48 (2 streams x 24)
Flow: 2000-2500 m3/day
Application: Demineralized water for power plant boiler application
QUA Solution
After evaluating the plant’s demineralization solution options, electrodeionization was chosen as the most viable option.
QUA’s Fractional Electrodeionization FEDI-2 30X SV stacks were chosen for the electrodeionization polishing step of the process after detailed technical and commercial evaluation.
QUA supplied 48 numbers of its FEDI 2 30X SV, in two streams of 24 stacks each. Each stream is in a three tier arrangement of 8 stacks. The FEDI stacks were installed in May 2013, and came into operation in mid-2014.
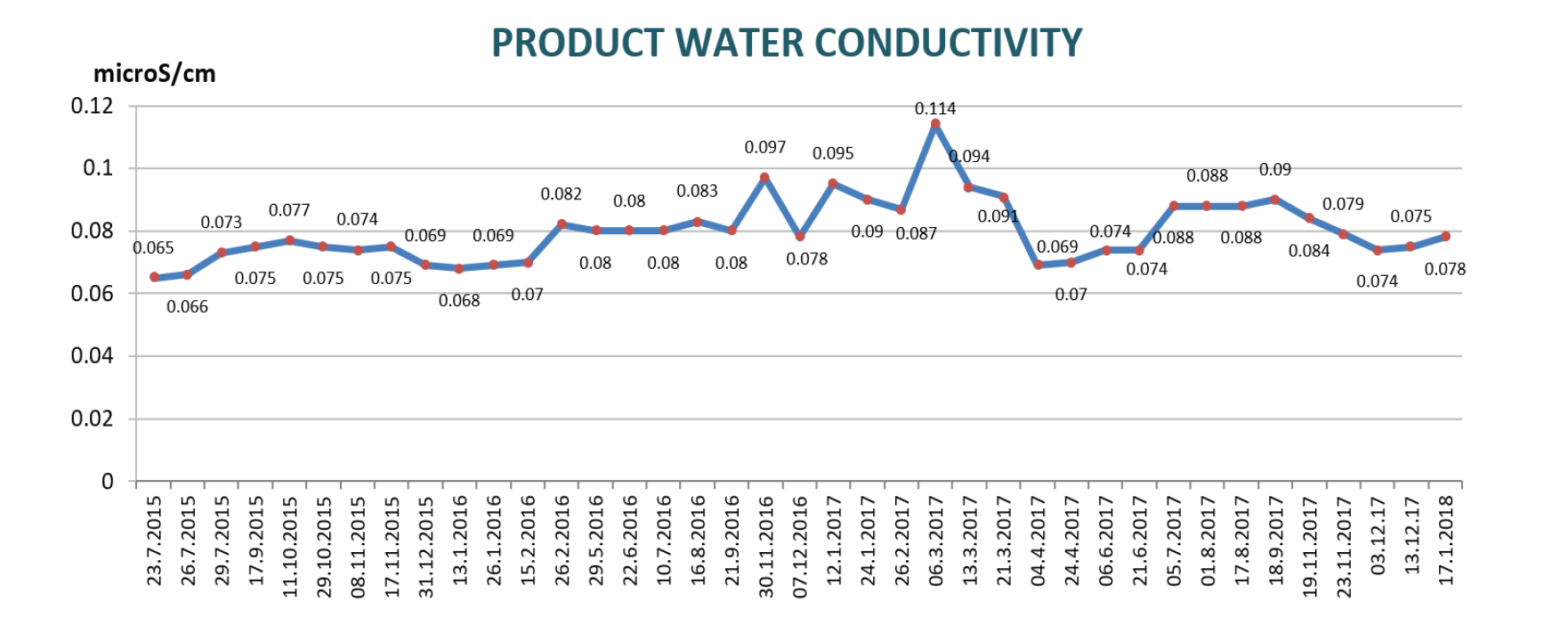
The FEDI system has been performing satisfactorily, since commissioning, for the last 5 years, and has been successfully delivering superior product water quality with low silica and conductivity levels. The client has been satisfied with the performance of the FEDI system.
The following graph presents the operational data product conductivity, which has been consistently less than 0.1 microS/cm.
About FEDI Technology
Electrodeionization is a continuous, chemical-free process that removes ionized and ionizable impurities from the feed water using DC power. EDI is most commonly used to treat reverse osmosis permeate and replaces Mixed Bed (MB) ion exchange; producing high purity water of up to 18 M Ω/cm. EDI eliminates the need to store and handle hazardous chemicals required for MB ion exchange resin regeneration and associated waste neutralization steps. EDI has a much lower space requirement, a low operating cost, and a quick return on investment in comparison to mixed bed; and produces high grade product water quality up to 18 M Ω/cm on a continuous and consistent basis.
Choosing an EDI system which will operate with single-pass RO feed water with less maintenance results in significant capital, space, and O&M savings that makes the solution effective and reliable.
After detailed evaluation of various EDI options, the customer found QUA® Fractional Electrodeionization (FEDI®) to be the only technology which could withstand hardness of 3 ppm as CaCO3 in the feed.
FEDI is an advancement in EDI technology which was developed to address the limitations of conventional EDI. FEDI’s patented dual voltage process allows for a higher flexibility and tolerance to inlet water conditions, thus lowering the risk of scaling, and improving the plant’s design economics and reliability.
The key difference between the two technologies is that rather than applying one current to the entire module as in conventional electrodeionization, the FEDI process differentiates the removal of weakly ionized and strongly ionized impurities by using a two-stage process. This allows a significant portion of strongly ionized impurities mainly the divalent ions which cause precipitation at higher voltage, to be removed in the first stage using lower current. Subsequently, a higher voltage is applied for removal of weakly ionized impurities such as silica in the second stage.
FEDI’s patented design maintains an acidic condition, thus reducing the scaling potential in the first stage and basic condition which helps in efficient removal of silica in the second stage of the EDI concentrate compartment.





